PaddleOCR-VL Usage Tutorial¶
PaddleOCR-VL is an advanced and efficient document parsing model designed specifically for element recognition in documents. Its core component is PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B, a compact yet powerful Vision-Language Model (VLM) composed of a NaViT-style dynamic resolution visual encoder and the ERNIE-4.5-0.3B language model, enabling precise element recognition. The model supports 109 languages and excels in recognizing complex elements (such as text, tables, formulas, and charts) while maintaining extremely low resource consumption. Comprehensive evaluations on widely used public benchmarks and internal benchmarks demonstrate that PaddleOCR-VL achieves SOTA performance in both page-level document parsing and element-level recognition. It significantly outperforms existing Pipeline-based solutions, document parsing multimodal schemes, and advanced general-purpose multimodal large models, while offering faster inference speeds. These advantages make it highly suitable for deployment in real-world scenarios.
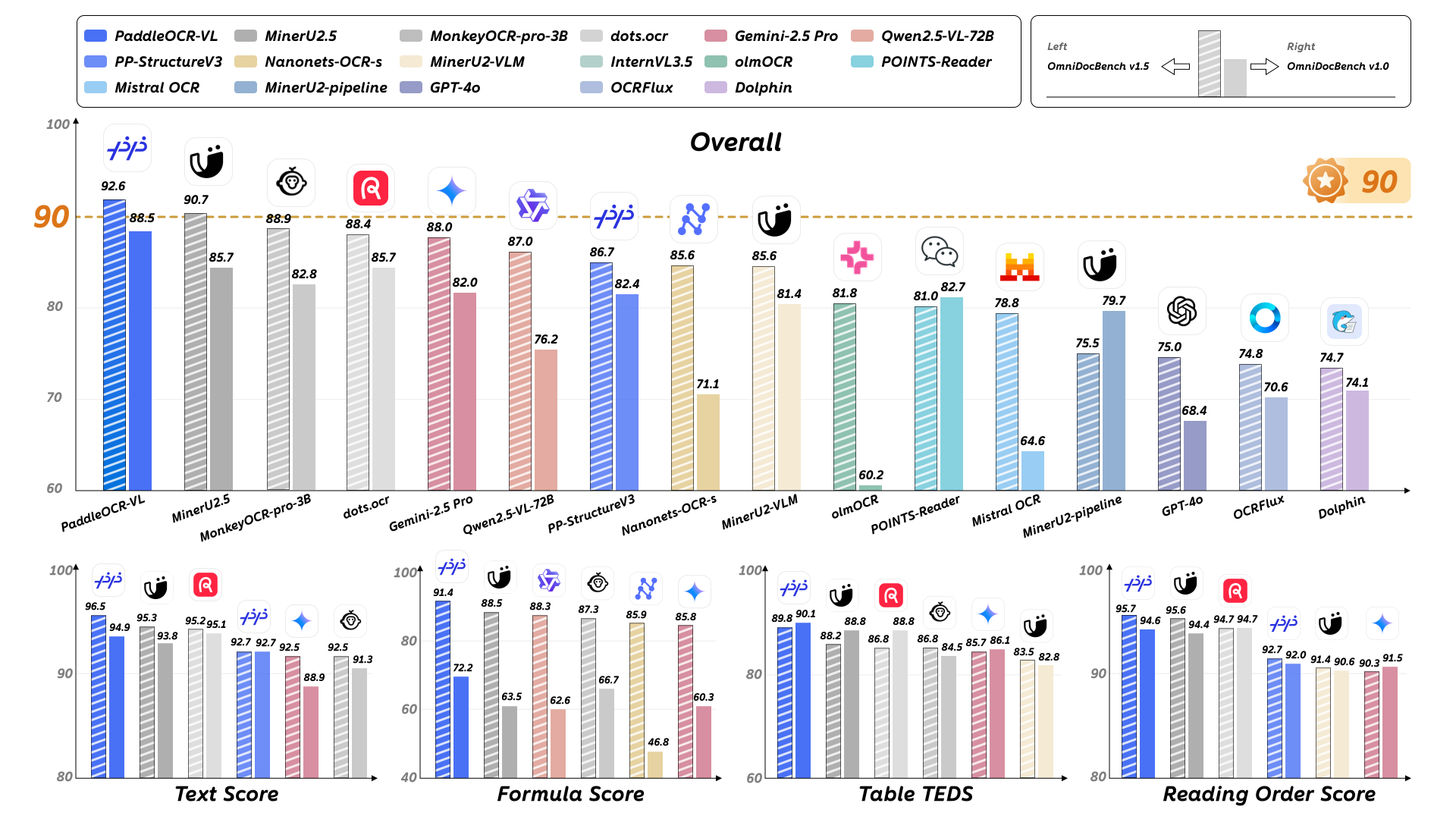
Process Guide¶
Before starting, please refer to the next section for information on the inference device support provided by PaddleOCR-VL to determine if your device meets the operational requirements. If your device meets the requirements, please select the relevant section to read based on your needs.
For some inference hardware, you may need to refer to other environment configuration documents we provide, but the process remains the same and does not affect your reading of the following process guide:
-
Want to quickly experience PaddleOCR-VL:
If you wish to quickly experience the inference effects of PaddleOCR-VL, please read 1. Environment Preparation and 2. Quick Start, or the corresponding chapters in documentation for other hardware.
-
Want to use PaddleOCR-VL in a production environment:
Although the quick experience allows you to feel the effects of PaddleOCR-VL, it may not be optimal in terms of inference speed and GPU memory usage. If you wish to apply PaddleOCR-VL in a production environment and have higher requirements for inference performance, please read 3. Enhancing VLM Inference Performance Using Inference Acceleration Frameworks or the corresponding chapter in documentation for other hardware.
-
Want to deploy PaddleOCR-VL as an API service:
If you want to deploy PaddleOCR-VL as a web service (API) so that other devices or applications can access and call it through a specific URL without configuring the environment, we offer two methods:
- Deployment using Docker Compose (one-click start, recommended): Please read 4.1 Method 1: Deploy Using Docker Compose and 4.3 Client-Side Invocation, or the corresponding chapters in documentation for other hardware.
- Manual deployment: Please read 1. Environment Preparation, 4.2 Method 2: Manual Deployment, and 4.3 Client-Side Invocation, or the corresponding chapters in documentation for other hardware.
-
Want to fine-tune PaddleOCR-VL to adapt to specific business needs:
If you find that the accuracy performance of PaddleOCR-VL in specific business scenarios does not meet expectations, please read 5. Model Fine-tuning or the corresponding chapter in documentation for other hardware.
Inference Device Support for PaddleOCR-VL¶
Currently, PaddleOCR-VL offers four inference methods, with varying levels of support for different inference devices. Please confirm that your inference device meets the requirements in the table below before proceeding with PaddleOCR-VL deployment:
| Inference Method | NVIDIA GPU | KUNLUNXIN XPU | HYGON DCU | MetaX GPU | Iluvatar GPU | x64 CPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | ✅ |
| vLLM | ✅ | 🚧 | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
| SGLang | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
| FastDeploy | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
Tip
- When using NVIDIA GPU for inference, ensure that the Compute Capability (CC) and CUDA version meet the requirements:
- PaddlePaddle: CC ≥ 7.0, CUDA ≥ 11.8
- vLLM: CC ≥ 8.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- SGLang: 8.0 ≤ CC < 12.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- FastDeploy: 8.0 ≤ CC < 12.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- Common GPUs with CC ≥ 8 include RTX 30/40/50 series and A10/A100, etc. For more models, refer to CUDA GPU Compute Capability
- vLLM compatibility note: Although vLLM can be launched on NVIDIA GPUs with CC 7.x such as T4/V100, timeout or OOM issues may occur, and its use is not recommended.
- Currently, PaddleOCR-VL does not support ARM architecture CPUs. More hardware support will be expanded based on actual needs in the future, so stay tuned!
- vLLM, SGLang, and FastDeploy cannot run natively on Windows or macOS. Please use the Docker images we provide.
Since different hardware requires different dependencies, if your hardware meets the requirements in the table above, please refer to the following table for the corresponding tutorial to configure your environment:
| Hardware Type | Environment Configuration Tutorial |
|---|---|
| x64 CPU | This tutorial |
| NVIDIA GPU | - NVIDIA Blackwell architecture GPU (e.g., RTX 50 series) refer to PaddleOCR-VL NVIDIA Blackwell Architecture GPU Environment Configuration Tutorial - Other NVIDIA GPUs refer to this tutorial |
| KUNLUNXIN XPU | PaddleOCR-VL XPU Environment Configuration Tutorial |
| HYGON DCU | PaddleOCR-VL DCU Environment Configuration Tutorial |
| MetaX GPU | PaddleOCR-VL MetaX GPU Environment Configuration Tutorial |
Tip
For example, if you are using an RTX 50 series GPU that meets the device requirements for both PaddlePaddle and vLLM inference methods, please refer to the PaddleOCR-VL NVIDIA Blackwell Architecture GPU Environment Configuration Tutorial to complete the environment configuration before using PaddleOCR-VL.
1. Environment Preparation¶
This section explains how to set up the runtime environment for PaddleOCR-VL. Choose one of the following two methods:
-
Method 1: Use the official Docker image.
-
Method 2: Manually install PaddlePaddle and PaddleOCR.
1.1 Method 1: Using Docker Image¶
We recommend using the official Docker image (requires Docker version >= 19.03, GPU-equipped machine with NVIDIA drivers supporting CUDA 12.6 or later):
docker run \
-it \
--gpus all \
--network host \
--user root \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest \
/bin/bash
# Invoke PaddleOCR CLI or Python API within the container
If you need to use PaddleOCR-VL in an offline environment, replace ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest (image size approximately 8 GB) in the above command with the offline version image ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline (image size is approximately 10 GB). You will need to pull the image on an internet-connected machine, import it into the offline machine, and then start the container using this image on the offline machine. For example:
# Execute on an internet-connected machine
docker pull ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline
# Save the image to a file
docker save ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline -o paddleocr-vl-latest-offline.tar
# Transfer the image file to the offline machine
# Execute on the offline machine
docker load -i paddleocr-vl-latest-offline.tar
# After that, you can use `docker run` to start the container on the offline machine
1.2 Method 2: Manually Install PaddlePaddle and PaddleOCR¶
If you cannot use Docker, you can manually install PaddlePaddle and PaddleOCR. The required Python version is 3.8–3.12.
We strongly recommend installing PaddleOCR-VL in a virtual environment to avoid dependency conflicts. For example, use the Python venv standard library to create a virtual environment:
# Create a virtual environment
python -m venv .venv_paddleocr
# Activate the environment
source .venv_paddleocr/bin/activate
Run the following commands to complete the installation:
# The following command installs the PaddlePaddle version for CUDA 12.6. For other CUDA versions and the CPU version, please refer to https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/zh/develop/install/pip/linux-pip.html
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.2.1 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu126/
python -m pip install -U "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
# For Linux systems, please directly copy and execute the following commands without modifying the cuda version in the link:
python -m pip install https://paddle-whl.bj.bcebos.com/nightly/cu126/safetensors/safetensors-0.6.2.dev0-cp38-abi3-linux_x86_64.whl
# For Windows systems, directly copy and execute the following command:
python -m pip install https://xly-devops.cdn.bcebos.com/safetensors-nightly/safetensors-0.6.2.dev0-cp38-abi3-win_amd64.whl
Important
Please ensure that you install PaddlePaddle framework version 3.2.1 or above, along with the special version of safetensors. For macOS users, please use Docker to set up the environment.
2. Quick Start¶
PaddleOCR-VL supports two usage methods: CLI command line and Python API. The CLI command line method is simpler and suitable for quickly verifying functionality, while the Python API method is more flexible and suitable for integration into existing projects.
Tip
The methods introduced in this section are primarily for rapid validation. Their inference speed, memory usage, and stability may not meet the requirements of a production environment. If deployment to a production environment is needed, we strongly recommend using a dedicated inference acceleration framework. For specific methods, please refer to the next section.
2.1 Command Line Usage¶
Run a single command to quickly test the PaddleOCR-VL :
# NVIDIA GPU
paddleocr doc_parser -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png
# KUNLUNXIN XPU
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --device xpu
# HYGON DCU
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --device dcu
# MetaX GPU
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --device metax_gpu
# Use --use_doc_orientation_classify to enable document orientation classification
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_doc_orientation_classify True
# Use --use_doc_unwarping to enable document unwarping module
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_doc_unwarping True
# Use --use_layout_detection to enable layout detection
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_layout_detection False
Command line supports more parameters. Click to expand for detailed parameter descriptions
| Parameter | Description | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
Meaning:Data to be predicted, required. Description: For example, the local path of an image file or PDF file: /root/data/img.jpg;Such as a URL link, for example, the network URL of an image file or PDF file:Example;Such as a local directory, which should contain the images to be predicted, for example, the local path: /root/data/(Currently, prediction for directories containing PDF files is not supported. PDF files need to be specified with a specific file path). |
str |
|
save_path |
Meaning:Specify the path where the inference result file will be saved. Description: If not set, the inference results will not be saved locally. |
str |
|
layout_detection_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the layout area detection and ranking model. Description: If not set, the default model of the production line will be used. |
str |
|
layout_detection_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the layout area detection and ranking model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str |
|
layout_threshold |
Meaning:Score threshold for the layout model. Description: Any value between 0-1. If not set, the default value is used, which is 0.5.
|
||
layout_nms |
Meaning:Whether to use post-processing NMS for layout detection. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
bool |
|
layout_unclip_ratio |
Meaning:Expansion coefficient for the detection boxes of the layout area detection model. Description: Any floating-point number greater than 0. If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
float |
|
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
Meaning:Merging mode for the detection boxes output by the model in layout detection. Description:
|
str |
|
vl_rec_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the multimodal recognition model. Description: If not set, the default model will be used. |
str |
|
vl_rec_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the multimodal recognition model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str |
|
vl_rec_backend |
Meaning:Inference backend used by the multimodal recognition model. | str |
|
vl_rec_server_url |
Description:If the multimodal recognition model uses an inference service, this parameter is used to specify the server URL. | str |
|
vl_rec_max_concurrency |
Meaning:If the multimodal recognition model uses an inference service, this parameter is used to specify the maximum number of concurrent requests. | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the document orientation classification model. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the document orientation classification model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str |
|
doc_unwarping_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the text image rectification model. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
str |
|
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the text image rectification model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the document orientation classification module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool |
|
use_doc_unwarping |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the text image rectification module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool |
|
use_layout_detection |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the layout area detection and ranking module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to True. |
bool |
|
use_chart_recognition |
Meaning:Whether to use the chart parsing function. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool |
|
format_block_content |
Meaning:Controls whether to format the block_content content within as Markdown. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which defaults to initialization as False. |
bool |
|
use_queues |
Meaning:Used to control whether to enable internal queues. Description: When set to True, data loading (such as rendering PDF pages as images), layout detection model processing, and VLM inference will be executed asynchronously in separate threads, with data passed through queues, thereby improving efficiency. This approach is particularly efficient for PDF documents with a large number of pages or directories containing a large number of images or PDF files. |
bool |
|
prompt_label |
Meaning:The prompt type setting for the VL model, which takes effect if and only if use_layout_detection=False. |
str |
|
repetition_penalty |
Meaning:The repetition penalty parameter used in VL model sampling. | float |
|
temperature |
Meaning:The temperature parameter used in VL model sampling. | float |
|
top_p |
Meaning:The top-p parameter used in VL model sampling. | float |
|
min_pixels |
Meaning:The minimum number of pixels allowed when the VL model preprocesses images. | int |
|
max_pixels |
Meaning:The maximum number of pixels allowed when the VL model preprocesses images. | int |
|
device |
Meaning:The device used for inference. Description: Supports specifying specific card numbers:
|
str |
|
enable_hpi |
Meaning:Whether to enable high-performance inference. | bool |
|
use_tensorrt |
Meaning:Whether to enable the TensorRT subgraph engine of Paddle Inference.
If the model does not support acceleration via TensorRT, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. For PaddlePaddle version with CUDA 11.8, the compatible TensorRT version is 8.x (x>=6). It is recommended to install TensorRT 8.6.1.6. |
bool |
|
precision |
Meaning:Computational precision, such as fp32, fp16. | str |
|
enable_mkldnn |
Meaning:Whether to enable MKL-DNN accelerated inference. Description: If MKL-DNN is not available or the model does not support acceleration via MKL-DNN, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. |
bool |
|
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
Meaning:MKL-DNN cache capacity. | int |
|
cpu_threads |
Meaning:The number of threads used for inference on the CPU. | int |
|
paddlex_config |
Meaning:The file path for PaddleX production line configuration. | str |
The inference result will be printed in the terminal. The default output of the PP-StructureV3 pipeline is as follows:
👉Click to expand
{'res': {'input_path': 'paddleocr_vl_demo.png', 'page_index': None, 'model_settings': {'use_doc_preprocessor': False, 'use_layout_detection': True, 'use_chart_recognition': False, 'format_block_content': False}, 'layout_det_res': {'input_path': None, 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 6, 'label': 'doc_title', 'score': 0.9636914134025574, 'coordinate': [np.float32(131.31366), np.float32(36.450516), np.float32(1384.522), np.float32(127.984665)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9281806349754333, 'coordinate': [np.float32(585.39465), np.float32(158.438), np.float32(930.2184), np.float32(182.57469)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9840355515480042, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.023666), np.float32(200.86115), np.float32(361.41583), np.float32(343.8828)]}, {'cls_id': 14, 'label': 'image', 'score': 0.9871416091918945, 'coordinate': [np.float32(775.50574), np.float32(200.66502), np.float32(1503.3807), np.float32(684.9304)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9801855087280273, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.532196), np.float32(344.90594), np.float32(361.4413), np.float32(440.8244)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9708921313285828, 'coordinate': [np.float32(28.040405), np.float32(455.87976), np.float32(341.7215), np.float32(520.7117)]}, {'cls_id': 24, 'label': 'vision_footnote', 'score': 0.9002962708473206, 'coordinate': [np.float32(809.0692), np.float32(703.70044), np.float32(1488.3016), np.float32(750.5238)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9825374484062195, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.896561), np.float32(536.54895), np.float32(361.05237), np.float32(655.8058)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9822263717651367, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.971573), np.float32(657.4949), np.float32(362.01715), np.float32(774.625)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9767460823059082, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.407074), np.float32(776.5216), np.float32(361.31067), np.float32(846.82874)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9868153929710388, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.669495), np.float32(848.2543), np.float32(361.64703), np.float32(1062.8568)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9826608300209045, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.8025055), np.float32(1063.8615), np.float32(361.46588), np.float32(1182.8524)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.982555627822876, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.820602), np.float32(1184.4663), np.float32(361.66394), np.float32(1302.4507)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9584776759147644, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.170288), np.float32(1304.2161), np.float32(361.48898), np.float32(1351.7483)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9782056212425232, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.1618), np.float32(200.38202), np.float32(742.7591), np.float32(295.65146)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9844875931739807, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.73303), np.float32(297.18463), np.float32(744.00024), np.float32(441.3034)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9680547714233398, 'coordinate': [np.float32(409.39468), np.float32(455.89386), np.float32(721.7174), np.float32(520.9387)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9741666913032532, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.71606), np.float32(536.8138), np.float32(742.7112), np.float32(608.00165)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9840384721755981, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.30988), np.float32(609.39636), np.float32(743.09247), np.float32(750.3231)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9845995306968689, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.13272), np.float32(751.7772), np.float32(743.058), np.float32(894.8815)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.984852135181427, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.83267), np.float32(896.0371), np.float32(743.58215), np.float32(1038.7345)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9804865717887878, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.08478), np.float32(1039.9119), np.float32(742.7585), np.float32(1134.4897)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.986461341381073, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.52643), np.float32(1135.8137), np.float32(743.451), np.float32(1352.0085)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9869391918182373, 'coordinate': [np.float32(769.8341), np.float32(775.66235), np.float32(1124.9813), np.float32(1063.207)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9822869896888733, 'coordinate': [np.float32(770.30383), np.float32(1063.938), np.float32(1124.8295), np.float32(1184.2192)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9689218997955322, 'coordinate': [np.float32(791.3042), np.float32(1199.3169), np.float32(1104.4521), np.float32(1264.6985)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9713128209114075, 'coordinate': [np.float32(770.4253), np.float32(1279.6072), np.float32(1124.6917), np.float32(1351.8672)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9236552119255066, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1153.9058), np.float32(775.5814), np.float32(1334.0654), np.float32(798.1581)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9857938885688782, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.5197), np.float32(799.28015), np.float32(1506.3619), np.float32(991.1156)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9820687174797058, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.5686), np.float32(991.91095), np.float32(1506.6023), np.float32(1110.8875)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9866049885749817, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.6919), np.float32(1112.1301), np.float32(1507.1611), np.float32(1351.9504)]}]}}}
For explanation of the result parameters, refer to 2.2 Python Script Integration.
Note: The default model for the pipeline is relatively large, which may result in slower inference speed. It is recommended to use inference acceleration frameworks to enhance VLM inference performance for faster inference.
2.2 Python Script Integration¶
The command line method is for quick testing and visualization. In actual projects, you usually need to integrate the model via code. You can perform pipeline inference with just a few lines of code as shown below:
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
# NVIDIA GPU
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
# KUNLUNXIN XPU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="xpu")
# HYGON DCU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="dcu")
# MetaX GPU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="metax_gpu")
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_doc_orientation_classify=True) # Use use_doc_orientation_classify to enable/disable document orientation classification model
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_doc_unwarping=True) # Use use_doc_unwarping to enable/disable document unwarping module
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_layout_detection=False) # Use use_layout_detection to enable/disable layout detection module
output = pipeline.predict("./paddleocr_vl_demo.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## Print the structured prediction output
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") ## Save the current image's structured result in JSON format
res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output") ## Save the current image's result in Markdown format
For PDF files, each page will be processed individually and generate a separate Markdown file. If you want to convert the entire PDF to a single Markdown file, use the following method:
from pathlib import Path
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
input_file = "./your_pdf_file.pdf"
output_path = Path("./output")
# NVIDIA GPU
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
# KUNLUNXIN XPU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="xpu")
# HYGON DCU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="dcu")
# MetaX GPU
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(device="metax_gpu")
output = pipeline.predict(input=input_file)
markdown_list = []
markdown_images = []
for res in output:
md_info = res.markdown
markdown_list.append(md_info)
markdown_images.append(md_info.get("markdown_images", {}))
markdown_texts = pipeline.concatenate_markdown_pages(markdown_list)
mkd_file_path = output_path / f"{Path(input_file).stem}.md"
mkd_file_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with open(mkd_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(markdown_texts)
for item in markdown_images:
if item:
for path, image in item.items():
file_path = output_path / path
file_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
image.save(file_path)
Note:
- In the example code, the parameters
use_doc_orientation_classifyanduse_doc_unwarpingare all set toFalseby default. These indicate that document orientation classification and document image unwarping are disabled. You can manually set them toTrueif needed.
The above Python script performs the following steps:
(1) Instantiate the pipeline object. Specific parameter descriptions are as follows:
| Parameter | Parameter Description | Parameter Type | Default Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
layout_detection_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the layout area detection and ranking model. Description: If set to None, the default model of the production line will be used. |
str|None |
None |
|
layout_detection_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the layout area detection and ranking model. Description: If set to None, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
|
layout_threshold |
Meaning:Score threshold for the layout model. Description:
| float|dict|None |
None |
|
layout_nms |
Meaning:Whether to use post-processing NMS for layout detection. Description: If set to None, the parameter value initialized by the production line will be used. |
bool|None |
None |
|
layout_unclip_ratio |
Meaning:Expansion coefficient for the detection box of the layout area detection model. Description:
| float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
|
layout_merge_bboxes_mode
Meaning:Merging mode for the detection boxes output by the model in layout detection. |
Description: str|dict|NoneNone | |||
vl_rec_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the multimodal recognition model. Description: If not set, the default model will be used. |
str|None |
None |
|
vl_rec_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the multimodal recognition model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
|
vl_rec_backend |
Meaning:Inference backend used by the multimodal recognition model. | str|None |
None |
|
vl_rec_server_url |
Meaning:If the multimodal recognition model uses an inference service, this parameter is used to specify the server URL. | str|None |
None |
|
vl_rec_max_concurrency |
Meaning:If the multimodal recognition model uses an inference service, this parameter is used to specify the maximum number of concurrent requests. | str|None |
None |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the document orientation classification model. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
str|None |
None |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the document orientation classification model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
|
doc_unwarping_model_name |
Meaning:Name of the text image rectification model. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used. |
str|None |
None |
|
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
Meaning:Directory path of the text image rectification model. Description: If not set, the official model will be downloaded. |
str|None |
None |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the document orientation classification module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool|None |
None |
|
use_doc_unwarping |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the text image rectification module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool|None |
None |
|
use_layout_detection |
Meaning:Whether to load and use the layout area detection and ranking module. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to True. |
bool|None |
None |
|
use_chart_recognition |
Meaning:Whether to use the chart parsing function. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which is initialized to False. |
bool|None |
None |
|
format_block_content |
Meaning:Controls whether to format the block_content content within as Markdown. Description: If not set, the initialized default value will be used, which defaults to initialization as False. |
bool|None |
None |
|
device |
Meaning:The device used for inference. Description: Supports specifying specific card numbers:
|
str|None |
None |
|
enable_hpi |
Meaning:Whether to enable high-performance inference. | bool |
False |
|
use_tensorrt |
Meaning:Whether to enable the TensorRT subgraph engine of Paddle Inference. Description: If the model does not support acceleration via TensorRT, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. For PaddlePaddle version with CUDA 11.8, the compatible TensorRT version is 8.x (x>=6). It is recommended to install TensorRT 8.6.1.6. |
bool |
False |
|
precision |
Meaning:Computational precision, such as fp32, fp16. | str |
"fp32" |
|
enable_mkldnn |
Meaning:Whether to enable MKL-DNN accelerated inference. Description: If MKL-DNN is not available or the model does not support acceleration via MKL-DNN, acceleration will not be used even if this flag is set. |
bool |
True |
|
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
Meaning:MKL-DNN cache capacity. | int |
10 |
|
cpu_threads |
Meaning:The number of threads used for inference on the CPU. | int |
8 |
|
paddlex_config |
Meaning:The file path for PaddleX production line configuration. | str |
None |
(2) Call the predict()method of the PaddleOCR-VL pipeline object for inference prediction. This method will return a list of results. Additionally, the pipeline also provides the predict_iter()Method. The two are completely consistent in terms of parameter acceptance and result return. The difference lies in that predict_iter()returns a generator, which can process and obtain prediction results step by step. It is suitable for scenarios involving large datasets or where memory conservation is desired. You can choose either of these two methods based on actual needs. Below are the parameters of the predict()method and their descriptions:
| Parameter | Parameter Description | Parameter Type | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
Meaning:Data to be predicted, supporting multiple input types. Required. Description:
|
Python Var|str|list |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
Meaning:Whether to use the document orientation classification module during inference. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
Meaning:Whether to use the text image rectification module during inference. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
use_layout_detection |
Meaning:Whether to use the layout region detection and sorting module during inference. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
use_chart_recognition |
Meaning:Whether to use the chart parsing module during inference. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
layout_threshold |
Meaning:The parameter meaning is basically the same as the instantiation parameter. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
float|dict|None |
None |
layout_nms |
Meaning:The parameter meaning is basically the same as the instantiation parameter. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
layout_unclip_ratio |
Meaning:The parameter meaning is basically the same as the instantiation parameter. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
Meaning:The parameter meaning is basically the same as the instantiation parameter. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
str|dict|None |
None |
use_queues |
Meaning:Used to control whether to enable internal queues. Description: When set to True, data loading (such as rendering PDF pages as images), layout detection model processing, and VLM inference will be executed asynchronously in separate threads, with data passed through queues, thereby improving efficiency. This approach is particularly efficient for PDF documents with many pages or directories containing a large number of images or PDF files. |
bool|None |
None |
prompt_label |
Meaning:The prompt type setting for the VL model, which takes effect only when use_layout_detection=False. |
str|None |
None |
format_block_content |
Meaning:The parameter meaning is basically the same as the instantiation parameter. Description: Setting it to None means using the instantiation parameter; otherwise, this parameter takes precedence. |
bool|None |
None |
repetition_penalty |
Meaning:The repetition penalty parameter used for VL model sampling. | float|None |
None |
temperature |
Meaning:Temperature parameter used for VL model sampling. | float|None |
None |
top_p |
Meaning:Top-p parameter used for VL model sampling. | float|None |
None |
min_pixels |
Meaning:The minimum number of pixels allowed when the VL model preprocesses images. | int|None |
None |
max_pixels |
Meaning:The maximum number of pixels allowed when the VL model preprocesses images. | int|None |
None |
(3) Process the prediction results: The prediction result for each sample is a corresponding Result object, supporting operations such as printing, saving as an image, and saving as a json file:
| Method | Method Description | Parameter | Parameter Type | Parameter Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
print() |
Print results to the terminal | format_json |
bool |
Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation. |
True |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable. Only valid when format_json is True. |
4 |
||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non- ASCII characters are escaped as Unicode. When set to True, all non- ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Only valid when format_json is True. |
False |
||
save_to_json() |
Save the results as a json format file | save_path |
str |
The file path for saving. When it is a directory, the saved file name will be consistent with the input file type naming. | None |
indent |
int |
Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSONdata, making it more readable. Only valid when format_jsonis True. |
4 |
||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
Control whether non- ASCII characters are escaped as Unicode. When set to True, all non- ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters. Only valid when format_json is True. |
False |
||
save_to_img() |
Save the visualized images of each intermediate module in png format | save_path |
str |
The file path for saving, supporting directory or file paths. | None |
save_to_markdown() |
Save each page in an image or PDF file as a markdown format file separately | save_path |
str |
The file path for saving. When it is a directory, the saved file name will be consistent with the input file type naming | None |
pretty |
bool |
Whether to beautify the markdown output results, centering charts, etc., to make the markdown rendering more aesthetically pleasing. |
True |
||
show_formula_number |
bool |
Control whether to retain formula numbers in markdown. When set to True, all formula numbers are retained; False retains only the formulas |
False |
||
save_to_html() |
Save the tables in the file as html format files | save_path |
str |
The file path for saving, supporting directory or file paths. | None |
save_to_xlsx() |
Save the tables in the file as xlsx format files | save_path |
str |
The file path for saving, supporting directory or file paths. | None |
- Calling the
print()method will print the results to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows:input_path:(str)The input path of the image or PDF to be predicted.page_index:(Union[int, None])If the input is a PDF file, it indicates the current page number of the PDF; otherwise, it isNone.model_settings:(Dict[str, bool])Model parameters required for configuring PaddleOCR-VL.use_doc_preprocessor:(bool)Controls whether to enable the document preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_layout_detection:(bool)Control whether to enable the layout detection module.use_chart_recognition:(bool)Controls whether to enable the chart recognition function.format_block_content:(bool)Control whether to save formatted markdown content inJSON.
doc_preprocessor_res:(Dict[str, Union[str, Dict[str, bool], int]])A dictionary of document preprocessing results, which exists only whenuse_doc_preprocessor=True.input_path:(str)The image path accepted by the document preprocessing sub-pipeline. When the input is anumpy.ndarray, it is saved asNone; here, it isNone.page_index:NoneSince the input here is anumpy.ndarray, the value isNonemodel_settings:(Dict[str, bool])Model configuration parameters for the document preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_doc_orientation_classify:(bool)Controls whether to enable the document image orientation classification sub-module.use_doc_unwarping:(bool)Controls whether to enable the text image distortion correction sub-module.
angle:(int)The prediction result of the document image orientation classification sub-module. When enabled, it returns the actual angle value.
parsing_res_list:(List[Dict])A list of parsing results, where each element is a dictionary. The list order is the reading order after parsing.block_bbox:(np.ndarray)The bounding box of the layout area.block_label:(str)The label of the layout area, such astext,table, etc.block_content:(str)The content within the layout area.block_id:(int)The index of the layout area, used to display the layout sorting results.block_order:(int)The order of the layout area, used to display the layout reading order. For non-sorted parts, the default value isNone.
- Calling the
save_to_json()method will print the results to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows: -
input_path:(str)The input path of the image or PDF to be predicted.page_index:(Union[int, None])If the input is a PDF file, it indicates the current page number of the PDF; otherwise, it isNonemodel_settings:(Dict[str, bool])Model parameters required for configuring PaddleOCR-VL.use_doc_preprocessor:(bool)Controls whether to enable the document preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_layout_detection:(bool)Controls whether to enable the layout detection module.use_chart_recognition:(bool)Controls whether to enable the chart recognition module.format_block_content:(bool)Controls whether to save the formatted markdown content in theJSONfile.
doc_preprocessor_res:(Dict[str, Union[str, Dict[str, bool], int]])A dictionary of document preprocessing results, which exists only whenuse_doc_preprocessor=Trueinput_path:(str)The image path accepted by the document preprocessing sub-pipeline. When the input is anumpy.ndarray, it is saved asNone; here, it isNonepage_index:NoneSince the input here is anumpy.ndarray, the value isNonemodel_settings:(Dict[str, bool])Model configuration parameters for the document preprocessing sub-pipeline.use_doc_orientation_classify:(bool)Controls whether to enable the document image orientation classification sub-module.use_doc_unwarping:(bool)Controls whether to enable the text image unwarping sub-module.
angle:(int)The predicted angle value of the document image orientation classification sub-module, which is returned when enabled.
parsing_res_list:(List[Dict])A list of parsing results, where each element is a dictionary. The order of the list is the reading order after parsing.block_bbox:(np.ndarray)The bounding box coordinates of the layout region.block_label:(str)The label of the layout region, such astext,table, etc.block_content:(str)The content of the layout region, which is the text or table content within the region.block_id:(int)The index of the layout region, which is used to display the layout sorting results.block_order:(int)The order of the layout region, which is used to display the layout reading order. For non-ordered regions, the default value isNone.
- Calling the
save_to_img()method will save the visualization results to the specifiedsave_path. If a directory is specified, visualized images for layout region detection, global OCR, layout reading order, etc., will be saved. If a file is specified, it will be saved directly to that file. (Production lines typically contain many result images, so it is not recommended to directly specify a specific file path, as multiple images will be overwritten, retaining only the last one.) - Calling the
save_to_markdown()method will save the converted Markdown file to the specifiedsave_path. The saved file path will besave_path/{your_img_basename}.md. If the input is a PDF file, it is recommended to directly specify a directory; otherwise, multiple markdown files will be overwritten.
| Attribute | Attribute Description |
|---|---|
json |
Obtain the prediction jsonresult in the format |
img |
obtain in the format of dictvisualized image |
markdown |
obtain in the format of dictmarkdown result |
- The prediction result obtained through the
jsonattribute is data of dict type, with relevant content consistent with that saved by calling thesave_to_json()method. - The prediction result returned by the
imgattribute is data of dict type. The keys arelayout_det_res,overall_ocr_res,text_paragraphs_ocr_res,formula_res_region1,table_cell_img, andseal_res_region1, with corresponding values beingImage.Imageobjects: used to display visualized images of layout region detection, OCR, OCR text paragraphs, formulas, tables, and seal results, respectively. If optional modules are not used, the dict only containslayout_det_res. - The prediction result returned by the
markdownattribute is data of dict type. The keys aremarkdown_texts,markdown_images, andpage_continuation_flags, with corresponding values being markdown text, images displayed in Markdown (Image.Imageobjects), and a bool tuple used to identify whether the first element on the current page is the start of a paragraph and whether the last element is the end of a paragraph, respectively.
3. Enhancing VLM Inference Performance Using Inference Acceleration Frameworks¶
The inference performance under default configurations is not fully optimized and may not meet actual production requirements. This step primarily introduces how to use the vLLM, SGLang and FastDeploy inference acceleration frameworks to enhance the inference performance of PaddleOCR-VL.
3.1 Launching the VLM Inference Service¶
There are two methods to launch the VLM inference service; choose either one:
-
Method 1: Launch the service using the official Docker image.
-
Method 2: Launch the service by manually installing dependencies via the PaddleOCR CLI.
3.1.1 Method 1: Using Docker Image¶
PaddleOCR provides Docker images for quickly launching vLLM or FastDeploy inference services. You can use the following commands to start the services (requires Docker version >= 19.03, a machine equipped with a GPU, and NVIDIA drivers supporting CUDA 12.6 or later):
docker run \
-it \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8118 --backend vllm
If you wish to start the service in an environment without internet access, replace ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest (image size approximately 13 GB) in the above command with the offline version image ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest-offline (image size approximately 15 GB).
docker run \
-it \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8118 --backend fastdeploy
If you wish to start the service in an environment without internet access, replace ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest (image size approximately 43 GB) in the above command with the offline version image ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest-offline (image size approximately 45 GB).
When starting the vLLM or FastDeploy inference service, we provide a set of default parameter settings. If you have additional requirements for adjusting parameters such as GPU memory usage, you can configure more parameters yourself. Please refer to 3.3.1 Server-side Parameter Adjustment to create a configuration file, then mount this file into the container, and specify the configuration file using backend_config in the command to start the service. Taking vLLM as an example:
docker run \
-it \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
-v vllm_config.yml:/tmp/vllm_config.yml \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8118 --backend vllm --backend_config /tmp/vllm_config.yml
3.1.2 Method 2: Installation and Usage via PaddleOCR CLI¶
Since inference acceleration frameworks may have dependency conflicts with the PaddlePaddle framework, it is recommended to install them in a virtual environment. Taking vLLM as an example:
# If there is an active virtual environment currently, deactivate it first using `deactivate`
# Create a virtual environment
python -m venv .venv_vlm
# Activate the environment
source .venv_vlm/bin/activate
# Install PaddleOCR
python -m pip install "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
# Install dependencies for the inference acceleration service
paddleocr install_genai_server_deps vllm
Usage of the paddleocr install_genai_server_deps command:
Currently supported framework names are vllm, sglang and fastdeploy, corresponding to vLLM, SGLang and FastDeploy, respectively.
The vLLM and SGLang installed via paddleocr install_genai_server_deps are both CUDA 12.6 versions; ensure that your local NVIDIA drivers are consistent with or higher than this version.
The
paddleocr install_genai_server_depscommand may require CUDA compilation tools such as nvcc during execution. If these tools are not available in your environment (e.g., when using thepaddleocr-vlimage), you can obtain a precompiled version of FlashAttention from this repository. Install the precompiled package before executing subsequent commands. For example, if you are in thepaddleocr-vlimage, executepython -m pip install https://github.com/mjun0812/flash-attention-prebuild-wheels/releases/download/v0.3.14/flash_attn-2.8.2+cu128torch2.8-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl.
After installation, you can launch the service using the paddleocr genai_server command:
The parameters supported by this command are as follows:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
--model_name |
Model name |
--model_dir |
Model directory |
--host |
Server hostname |
--port |
Server port number |
--backend |
Backend name, i.e., the name of the inference acceleration framework used; options are vllm or sglang |
--backend_config |
Can specify a YAML file containing backend configurations |
3.2 Client Usage Methods¶
After launching the VLM inference service, the client can call the service through PaddleOCR. Please note that because the client needs to invoke the sequential model for layout detection, it is still recommended to run the client on GPU or other acceleration devices to achieve more stable and efficient performance.
3.2.1 CLI Invocation¶
Specify the backend type (vllm-server or sglang-server) using --vl_rec_backend and the service address using --vl_rec_server_url, for example:
paddleocr doc_parser --input paddleocr_vl_demo.png --vl_rec_backend vllm-server --vl_rec_server_url http://127.0.0.1:8118/v1
3.2.2 Python API Invocation¶
Pass the vl_rec_backend and vl_rec_server_url parameters when creating a PaddleOCRVL object:
3.3 Performance Tuning¶
The default configurations are optimized for single NVIDIA A100 GPUs with exclusive client access and may not be suitable for other environments. If users encounter performance issues in actual use, the following optimization methods can be attempted.
3.3.1 Server-Side Parameter Adjustment¶
Different inference acceleration frameworks support different parameters. Refer to their official documentation for available parameters and adjustment timing:
- vLLM Official Parameter Tuning Guide
- SGLang Hyperparameter Tuning Documentation
- FastDeploy Best Practices
The PaddleOCR VLM inference service supports parameter tuning through configuration files. The following example shows how to adjust the gpu-memory-utilization and max-num-seqs parameters for the vLLM server:
- Create a YAML file
vllm_config.yamlwith the following content:
- Specify the configuration file path when starting the service, for example, using the
paddleocr genai_servercommand:
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --backend vllm --backend_config vllm_config.yaml
If using a shell that supports process substitution (like Bash), you can also pass configuration items directly without creating a configuration file:
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --backend vllm --backend_config <(echo -e 'gpu-memory-utilization: 0.3\nmax-num-seqs: 128')
3.3.2 Client-Side Parameter Adjustment¶
PaddleOCR groups sub-images from single or multiple input images and sends concurrent requests to the server, so the number of concurrent requests significantly impacts performance.
- For CLI and Python API, adjust the maximum number of concurrent requests using the
vl_rec_max_concurrencyparameter; - For service deployment, modify the
VLRecognition.genai_config.max_concurrencyfield in the configuration file.
When there is a 1:1 client-to-VLM inference service ratio and sufficient server resources, increasing concurrency can improve performance. If the server needs to support multiple clients or has limited computing resources, reduce concurrency to avoid resource overload and service abnormalities.
3.3.3 Common Hardware Performance Tuning Recommendations¶
The following configurations are for scenarios with a 1:1 client-to-VLM inference service ratio.
NVIDIA RTX 3060
- Server-Side
- vLLM:
gpu-memory-utilization: 0.8 - FastDeploy:
gpu-memory-utilization: 0.8max-concurrency: 2048
- vLLM:
4. Service Deployment¶
This step mainly introduces how to deploy PaddleOCR-VL as a service and invoke it. There are two methods; choose either one:
-
Method 1: Deploy using Docker Compose (recommended).
-
Method 2: Manual Deployment.
Note that the PaddleOCR-VL service described in this section differs from the VLM inference service in the previous section: the latter is responsible for only one part of the complete process (i.e., VLM inference) and is called as an underlying service by the former.
4.1 Method 1: Deploy Using Docker Compose (Recommended)¶
You can obtain the Compose file and the environment variables configuration file from here and here, respectively, and download them to your local machine. Then, in the directory where the files were just downloaded, execute the following command to start the server, which will listen on port 8080 by default:
After startup, you will see output similar to the following:
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Started server process [1]
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Waiting for application startup.
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Application startup complete.
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
This solution accelerates VLM inference based on frameworks like vLLM, making it more suitable for production environment deployment. However, it requires the machine to be equipped with a GPU and the NVIDIA driver to support CUDA 12.6 or higher.
Additionally, after starting the server using this method, no internet connection is required except for pulling the image. For offline environment deployment, you can first pull the images involved in the Compose file on an online machine, export and transfer them to the offline machine for import, and then start the service in the offline environment.
Docker Compose starts two containers in sequence by reading the configurations in the .env and compose.yaml files, running the underlying VLM inference service and the PaddleOCR-VL service (Pipeline) respectively.
The meanings of each environment variable contained in the .env file are as follows:
API_IMAGE_TAG_SUFFIX: The tag suffix of the image used to start the pipeline service. The default islatest-offline, indicating the use of an offline GPU image.VLM_BACKEND: The VLM inference backend, currently supportingvllmandfastdeploy. The default isvllm.VLM_IMAGE_TAG_SUFFIX: The tag suffix of the image used to start the VLM inference service. The default islatest-offline, indicating the use of an offline GPU image.
You can meet custom requirements by modifying .env and compose.yaml, for example:
1. Change the port of the PaddleOCR-VL service
Editpaddleocr-vl-api.ports in the compose.yaml file to change the port. For example, if you need to change the service port to 8111, make the following modifications:
2. Specify the GPU used by the PaddleOCR-VL service
Editdevice_ids in the compose.yaml file to change the GPU used. For example, if you need to use GPU card 1 for deployment, make the following modifications:
3. Adjust VLM server-side configuration
If you want to adjust the VLM server-side configuration, please refer to 3.3.1 Server-side Parameter Adjustment to generate a configuration file. After generating the configuration file, add the followingpaddleocr-vlm-server.volumes and paddleocr-vlm-server.command fields to your compose.yaml. Please replace /path/to/your_config.yaml with your actual configuration file path.
4. Change the VLM inference backend
ModifyVLM_BACKEND in the .env file, for example, to change the VLM inference backend to fastdeploy:
5. Adjust pipeline configurations (such as model path, batch size, deployment device, etc.)
Refer to section 4.4 Pipeline Configuration Adjustment Instructions in this document.4.2 Method 2: Manual Deployment¶
Execute the following command to install the service deployment plugin via the PaddleX CLI:
Then, start the server using the PaddleX CLI:
After startup, you will see output similar to the following, with the server listening on port 8080 by default:
INFO: Started server process [63108]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
The command-line options related to serving are as follows:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
--pipeline |
PaddleX pipeline registration name or pipeline configuration file path. |
--device |
Deployment device for the pipeline. By default, a GPU will be used if available; otherwise, a CPU will be used." |
--host |
Hostname or IP address to which the server is bound. Defaults to 0.0.0.0. |
--port |
Port number on which the server listens. Defaults to 8080. |
--use_hpip |
If specified, uses high-performance inference. Refer to the High-Performance Inference documentation for more information. |
--hpi_config |
High-performance inference configuration. Refer to the High-Performance Inference documentation for more information. |
If you need to adjust pipeline configurations (such as model path, batch size, deployment device, etc.), you can specify the --pipeline parameter as a custom configuration file path. For the correspondence between PaddleOCR pipelines and PaddleX pipeline registration names, as well as how to obtain and modify PaddleX pipeline configuration files, please refer to PaddleOCR and PaddleX. Furthermore, section 4.1.3 will introduce how to adjust the pipeline configuration based on common requirements.
4.3 Client-Side Invocation¶
Below are the API reference and examples of multi-language service invocation:
API Reference
Main operations provided by the service:
- The HTTP request method is POST.
- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON objects).
- When the request is processed successfully, the response status code is
200, and the properties of the response body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Fixed as 0. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. Fixed as "Success". |
result |
object |
Operation result. |
- When the request is not processed successfully, the properties of the response body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
The UUID of the request. |
errorCode |
integer |
Error code. Same as the response status code. |
errorMsg |
string |
Error description. |
The main operations provided by the service are as follows:
infer
Perform layout parsing.
POST /layout-parsing
- The properties of the request body are as follows:
| Name | Type | Meaning | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
file |
string |
The URL of an image file or PDF file accessible to the server, or the Base64-encoded result of the content of the aforementioned file types. By default, for PDF files with more than 10 pages, only the first 10 pages will be processed. To remove the page limit, add the following configuration to the pipeline configuration file:
|
Yes |
fileType |
integer|null |
File type.0 represents a PDF file,1 represents an image file. If this property is not present in the request body, the file type will be inferred from the URL. |
No |
useDocOrientationClassify |
boolean | null |
Please refer to the description of the use_doc_orientation_classify parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
useDocUnwarping |
boolean|null |
Please refer to the description of the use_doc_unwarping parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
useLayoutDetection |
boolean|null |
Please refer to the description of the use_layout_detection parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
useChartRecognition |
boolean|null |
Please refer to the description of the use_chart_recognition parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
layoutThreshold |
number|object|null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_threshold parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
layoutNms |
boolean|null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_nms parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
layoutUnclipRatio |
number|array|object|null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_unclip_ratio parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
layoutMergeBboxesMode |
string|object|null |
Please refer to the description of the layout_merge_bboxes_mode parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
promptLabel |
string|null |
Please refer to the description of the prompt_label parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
formatBlockContent |
boolean|null |
Please refer to the description of the format_block_content parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
repetitionPenalty |
number|null |
Please refer to the description of the repetition_penalty parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
temperature |
number|null |
Please refer to the description of the temperature parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
topP |
number|null |
Please refer to the description of the top_p parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
minPixels |
number|null |
Please refer to the description of the min_pixels parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
maxPixels |
number|null |
Please refer to the description of the max_pixels parameter in the predict method of the PaddleOCR-VL object. |
No |
prettifyMarkdown |
boolean |
Whether to output beautified Markdown text. The default is true. |
No |
showFormulaNumber |
boolean |
Whether to include formula numbers in the output Markdown text. The default is false. |
No |
visualize |
boolean|null |
Whether to return visualization result images and intermediate images during the processing.
For example, add the following field in the configuration file: visualize parameter in the request body. If this parameter is not set in either the request body or the configuration file (or null is passed in the request body and the configuration file is not set), images will be returned by default. |
No |
- When the request is processed successfully, the
resultin the response body has the following attributes:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
layoutParsingResults |
array |
Layout parsing results. The array length is 1 (for image input) or the actual number of document pages processed (for PDF input). For PDF input, each element in the array represents the result of each actual page processed in the PDF file. |
dataInfo |
object |
Input data information. |
Each element inlayoutParsingResults is an object with the following attributes:
| Meaning | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
prunedResult |
object |
A simplified version of the res field in the JSON representation of the results generated by the predict method of the object, with the input_path and page_index fields removed. |
markdown |
object |
Markdown results. |
outputImages |
object|null |
Refer to the img property description of the prediction results. The image is in JPEG format and encoded using Base64. |
inputImage |
string|null |
Input image. The image is in JPEG format and encoded using Base64. |
markdownis an objectwith the following properties:
| Name | Type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
text |
string |
Markdown text. |
images |
object |
Key-value pairs of relative paths to Markdown images and Base64-encoded images. |
isStart |
boolean |
Whether the first element on the current page is the start of a paragraph. |
isEnd |
boolean |
Whether the last element on the current page is the end of a paragraph. |
Multi-Language Service Invocation Examples
Python
import base64
import requests
import pathlib
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing" # Service URL
image_path = "./demo.jpg"
# Encode the local image in Base64
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {
"file": image_data, # Base64-encoded file content or file URL
"fileType": 1, # File type, 1 indicates an image file
}
# Call the API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# Process the returned data from the interface
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
for i, res in enumerate(result["layoutParsingResults"]):
print(res["prunedResult"])
md_dir = pathlib.Path(f"markdown_{i}")
md_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
(md_dir / "doc.md").write_text(res["markdown"]["text"])
for img_path, img in res["markdown"]["images"].items():
img_path = md_dir / img_path
img_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
img_path.write_bytes(base64.b64decode(img))
print(f"Markdown document saved at {md_dir / 'doc.md'}")
for img_name, img in res["outputImages"].items():
img_path = f"{img_name}_{i}.jpg"
pathlib.Path(img_path).parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
with open(img_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(img))
print(f"Output image saved at {img_path}")
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost", 8080);
const std::string filePath = "./demo.jpg";
std::ifstream file(filePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
if (!file) {
std::cerr << "Error opening file: " << filePath << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(buffer.data(), static_cast(size));
std::string encodedFile = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["file"] = encodedFile;
jsonObj["fileType"] = 1;
auto response = client.Post("/layout-parsing", jsonObj.dump(), "application/json");
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
if (!result.is_object() || !result.contains("layoutParsingResults")) {
std::cerr << "Unexpected response format." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
const auto& results = result["layoutParsingResults"];
for (size_t i = 0; i < results.size(); ++i) {
const auto& res = results[i];
if (res.contains("prunedResult")) {
std::cout << "Layout result [" << i << "]: " << res["prunedResult"].dump() << std::endl;
}
if (res.contains("outputImages") && res["outputImages"].is_object()) {
for (auto& [imgName, imgBase64] : res["outputImages"].items()) {
std::string outputPath = imgName + "_" + std::to_string(i) + ".jpg";
fs::path pathObj(outputPath);
fs::path parentDir = pathObj.parent_path();
if (!parentDir.empty() && !fs::exists(parentDir)) {
fs::create_directories(parentDir);
}
std::string decodedImage = base64::from_base64(imgBase64.get());
std::ofstream outFile(outputPath, std::ios::binary);
if (outFile.is_open()) {
outFile.write(decodedImage.c_str(), decodedImage.size());
outFile.close();
std::cout << "Saved image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "Failed to save image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
} else {
std::cerr << "Request failed." << std::endl;
if (response) {
std::cerr << "HTTP status: " << response->status << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Response body: " << response->body << std::endl;
}
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Java
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode payload = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
payload.put("file", base64Image);
payload.put("fileType", 1);
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(JSON, payload.toString());
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode root = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = root.get("result");
JsonNode layoutParsingResults = result.get("layoutParsingResults");
for (int i = 0; i < layoutParsingResults.size(); i++) {
JsonNode item = layoutParsingResults.get(i);
int finalI = i;
JsonNode prunedResult = item.get("prunedResult");
System.out.println("Pruned Result [" + i + "]: " + prunedResult.toString());
JsonNode outputImages = item.get("outputImages");
outputImages.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(imgName -> {
try {
String imgBase64 = outputImages.get(imgName).asText();
byte[] imgBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(imgBase64);
String imgPath = imgName + "_" + finalI + ".jpg";
File outputFile = new File(imgPath);
File parentDir = outputFile.getParentFile();
if (parentDir != null && !parentDir.exists()) {
parentDir.mkdirs();
System.out.println("Created directory: " + parentDir.getAbsolutePath());
}
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile)) {
fos.write(imgBytes);
System.out.println("Saved image: " + imgPath);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Failed to save image: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
}
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with HTTP code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
Go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing"
filePath := "./demo.jpg"
fileBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading file: %v\n", err)
return
}
fileData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(fileBytes)
payload := map[string]interface{}{
"file": fileData,
"fileType": 1,
}
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error marshaling payload: %v\n", err)
return
}
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating request: %v\n", err)
return
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error sending request: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
fmt.Printf("Unexpected status code: %d\n", res.StatusCode)
return
}
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading response: %v\n", err)
return
}
type Markdown struct {
Text string `json:"text"`
Images map[string]string `json:"images"`
}
type LayoutResult struct {
PrunedResult map[string]interface{} `json:"prunedResult"`
Markdown Markdown `json:"markdown"`
OutputImages map[string]string `json:"outputImages"`
InputImage *string `json:"inputImage"`
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
LayoutParsingResults []LayoutResult `json:"layoutParsingResults"`
DataInfo interface{} `json:"dataInfo"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &respData); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error parsing response: %v\n", err)
return
}
for i, res := range respData.Result.LayoutParsingResults {
fmt.Printf("Result %d - prunedResult: %+v\n", i, res.PrunedResult)
mdDir := fmt.Sprintf("markdown_%d", i)
os.MkdirAll(mdDir, 0755)
mdFile := filepath.Join(mdDir, "doc.md")
if err := os.WriteFile(mdFile, []byte(res.Markdown.Text), 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error writing markdown file: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Markdown document saved at %s\n", mdFile)
}
for path, imgBase64 := range res.Markdown.Images {
fullPath := filepath.Join(mdDir, path)
if err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(fullPath), 0755); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating directory for markdown image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
imgBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(imgBase64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding markdown image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
if err := os.WriteFile(fullPath, imgBytes, 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error saving markdown image: %v\n", err)
}
}
for name, imgBase64 := range res.OutputImages {
imgBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(imgBase64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding output image %s: %v\n", name, err)
continue
}
filename := fmt.Sprintf("%s_%d.jpg", name, i)
if err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(filename), 0755); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating directory for output image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
if err := os.WriteFile(filename, imgBytes, 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error saving output image %s: %v\n", filename, err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Output image saved at %s\n", filename)
}
}
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
static readonly string inputFilePath = "./demo.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
byte[] fileBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(inputFilePath);
string fileData = Convert.ToBase64String(fileBytes);
var payload = new JObject
{
{ "file", fileData },
{ "fileType", 1 }
};
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
JArray layoutParsingResults = (JArray)jsonResponse["result"]["layoutParsingResults"];
for (int i = 0; i < layoutParsingResults.Count; i++)
{
var res = layoutParsingResults[i];
Console.WriteLine($"[{i}] prunedResult:\n{res["prunedResult"]}");
JObject outputImages = res["outputImages"] as JObject;
if (outputImages != null)
{
foreach (var img in outputImages)
{
string imgName = img.Key;
string base64Img = img.Value?.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(base64Img))
{
string imgPath = $"{imgName}_{i}.jpg";
byte[] imageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Img);
string directory = Path.GetDirectoryName(imgPath);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(directory) && !Directory.Exists(directory))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directory);
Console.WriteLine($"Created directory: {directory}");
}
File.WriteAllBytes(imgPath, imageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {imgPath}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
Node.js
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing';
const imagePath = './demo.jpg';
const fileType = 1;
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
const payload = {
file: encodeImageToBase64(imagePath),
fileType: fileType
};
axios.post(API_URL, payload)
.then(response => {
const results = response.data.result.layoutParsingResults;
results.forEach((res, index) => {
console.log(`\n[${index}] prunedResult:`);
console.log(res.prunedResult);
const outputImages = res.outputImages;
if (outputImages) {
Object.entries(outputImages).forEach(([imgName, base64Img]) => {
const imgPath = `${imgName}_${index}.jpg`;
const directory = path.dirname(imgPath);
if (!fs.existsSync(directory)) {
fs.mkdirSync(directory, { recursive: true });
console.log(`Created directory: ${directory}`);
}
fs.writeFileSync(imgPath, Buffer.from(base64Img, 'base64'));
console.log(`Output image saved at ${imgPath}`);
});
} else {
console.log(`[${index}] No outputImages.`);
}
});
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error during API request:', error.message || error);
});
PHP
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("file" => $image_data, "fileType" => 1);
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$result = json_decode($response, true)["result"]["layoutParsingResults"];
foreach ($result as $i => $item) {
echo "[$i] prunedResult:\n";
print_r($item["prunedResult"]);
if (!empty($item["outputImages"])) {
foreach ($item["outputImages"] as $img_name => $img_base64) {
$output_image_path = "{$img_name}_{$i}.jpg";
$directory = dirname($output_image_path);
if (!is_dir($directory)) {
mkdir($directory, 0777, true);
echo "Created directory: $directory\n";
}
file_put_contents($output_image_path, base64_decode($img_base64));
echo "Output image saved at $output_image_path\n";
}
} else {
echo "No outputImages found for item $i\n";
}
}
?>
4.4 Pipeline Configuration Adjustment Instructions¶
Note
If you do not need to adjust pipeline configurations, you can ignore this section.
Adjusting the PaddleOCR-VL configuration for service deployment involves only three steps:
- Obtain the configuration file
- Modify the configuration file
- Apply the configuration file
4.4.1 Obtain the Configuration File¶
If you are deploying using Docker Compose:
Download the corresponding pipeline configuration file based on the backend you are using:
- vLLM: pipeline_config_vllm.yaml
- FastDeploy: pipeline_config_fastdeploy.yaml
If you are deploying by manually installing dependencies:
Execute the following command to generate the pipeline configuration file:
4.4.2 Modify the Configuration File¶
Enhance VLM Inference Performance Using Acceleration Frameworks
To improve VLM inference performance using acceleration frameworks such as vLLM (refer to Section 2 for detailed instructions on starting the VLM inference service), modify the VLRecognition.genai_config.backend and VLRecognition.genai_config.server_url fields in the pipeline configuration file, as shown below:
The Docker Compose solution already uses an acceleration framework by default.
Enable Document Image Preprocessing Functionality
The service started with default configurations does not support document preprocessing. If a client attempts to invoke this functionality, an error message will be returned. To enable document preprocessing, set use_doc_preprocessor to True in the pipeline configuration file and start the service using the modified configuration file.
Disable Result Visualization Functionality
The service returns visualized results by default, which introduces additional overhead. To disable this functionality, add the following configuration to the pipeline configuration file (Serving is a top-level field):
Additionally, you can set the visualize field to false in the request body to disable visualization for a single request.
Configure Return of Image URLs
For visualized result images and images included in Markdown, the service returns them in Base64 encoding by default. To return images as URLs instead, add the following configuration to the pipeline configuration file (Serving is a top-level field):
Serving:
extra:
file_storage:
type: bos
endpoint: https://bj.bcebos.com
bucket_name: some-bucket
ak: xxx
sk: xxx
key_prefix: deploy
return_img_urls: True
Currently, storing generated images in Baidu Intelligent Cloud Object Storage (BOS) and returning URLs is supported. The parameters are described as follows:
endpoint: Access domain name (required).ak: Baidu Intelligent Cloud Access Key (required).sk: Baidu Intelligent Cloud Secret Key (required).bucket_name: Storage bucket name (required).key_prefix: Unified prefix for object keys.connection_timeout_in_mills: Request timeout in milliseconds.
For more information on obtaining AK/SK and other details, refer to the Baidu Intelligent Cloud Official Documentation.
Modify PDF Parsing Page Limit
For performance considerations, the service processes only the first 10 pages of received PDF files by default. To adjust the page limit, add the following configuration to the pipeline configuration file (Serving is a top-level field):
Set max_num_input_imgs to null to remove the page limit.
4.4.3 Apply the Configuration File¶
If you deployed using Docker Compose:
If you are deploying using Docker Compose:
Set the services.paddleocr-vl-api.volumes field in the Compose file to mount the pipeline configuration file to the /home/paddleocr directory. For example:
services:
paddleocr-vl-api:
...
volumes:
- pipeline_config_vllm.yaml:/home/paddleocr/pipeline_config.yaml
...
In a production environment, you can also build the image yourself and package the configuration file into the image.
If you are deploying by manually installing dependencies:
When starting the service, specify the --pipeline parameter as the path to your custom configuration file.
5. Model Fine-Tuning¶
If you find that PaddleOCR-VL does not meet accuracy expectations in specific business scenarios, we recommend using the ERNIEKit suite to perform supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on the PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B model. For detailed instructions, refer to the ERNIEKit Official Documentation.
Currently, fine-tuning of layout detection and ranking models is not supported.